Knowing how to make your own electricity opens up a world of potential. It’s key to living off-grid but also can help with creating the ultimate home backup power system. And it’s never been easier.
Making renewable energy at home usually starts with solar power. You can also generate electricity with water, wind, or waste. And even though they still rely on non-renewable sources, fuel generators can still be useful.
And after reading this, you’ll be able to decide which source you should work with. We also will go over the best combinations for stable off-grid energy that can power any home indefinitely or during grid outages.
We carefully select the products and services we link to. If you buy through our links, we may earn a commission. There’s no extra cost to you and it helps us provide this information.

Solar Power Solutions: Turning Rays into Watts
When you want a long-lasting and low-maintenance way to create energy, it’s hard to beat solar. Set it in the sun and let it crank out the electrons.
There’s no limit to what you can power with solar panels. If you have sunlight and can afford them, solar panels are an easy way to generate electricity anywhere. Plus, they connect to all sorts of battery supplies, including solar generators.
Solar Basics
Solar panels capture sunlight with photovoltaic cells, usually made from silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it knocks electrons loose from their atoms. And this generates an electrical current, aka electricity.
The amount of energy solar panels generate depends on the size of the solar panels. The larger the panels, the more sunlight they absorb, and the more energy they generate.
Solar panels are measured in watts, typically anywhere from ~100W to ~400W. You can connect multiple solar panels to create powerful solar panel arrays. You need to know:
- What solar panel system size you need
- How to connect solar panels

Advantages of Solar Power
The best parts of creating your own power with solar are:
- The sky’s the limit: With the right amount of solar panels, you can create enough energy for entire houses, including heavy-duty appliances.
- Set it and forget it: Once installed, solar panels need very little maintenance or upkeep. If the sun shines, you have energy.
- Zero noise or emissions: Unlike many other ways to generate electricity, solar panels make no noise and emit no harmful toxins.
Solar panels are one of the most popular ways to make renewable energy at home. And that’s not a fluke. They are impressive and easy. They also have a carbon footprint of 10 to 20 times less than conventional energy generation. And they can be recycled to provide even more carbon savings.
Downsides to Solar Power
Like every energy source, there are downsides to solar. The main ones are:
- Sunlight required: If you don’t have direct sunlight, they won’t function. You need a sunny spot where you can install fixed solar panels and set out portable ones.
- Upfront investment: You pay for your energy in advance with solar. They’re a long-term investment with a lifetime of 20-30 years.
If you can overcome these challenges, you’ll be able to make a great solar-powered system no matter where you are.
Note: Batteries allow solar power to work at night. The panels charge the battery or solar generator when the sun shines. Then the battery powers your devices whether the sun is shining or not. The larger the battery, the longer it can last.
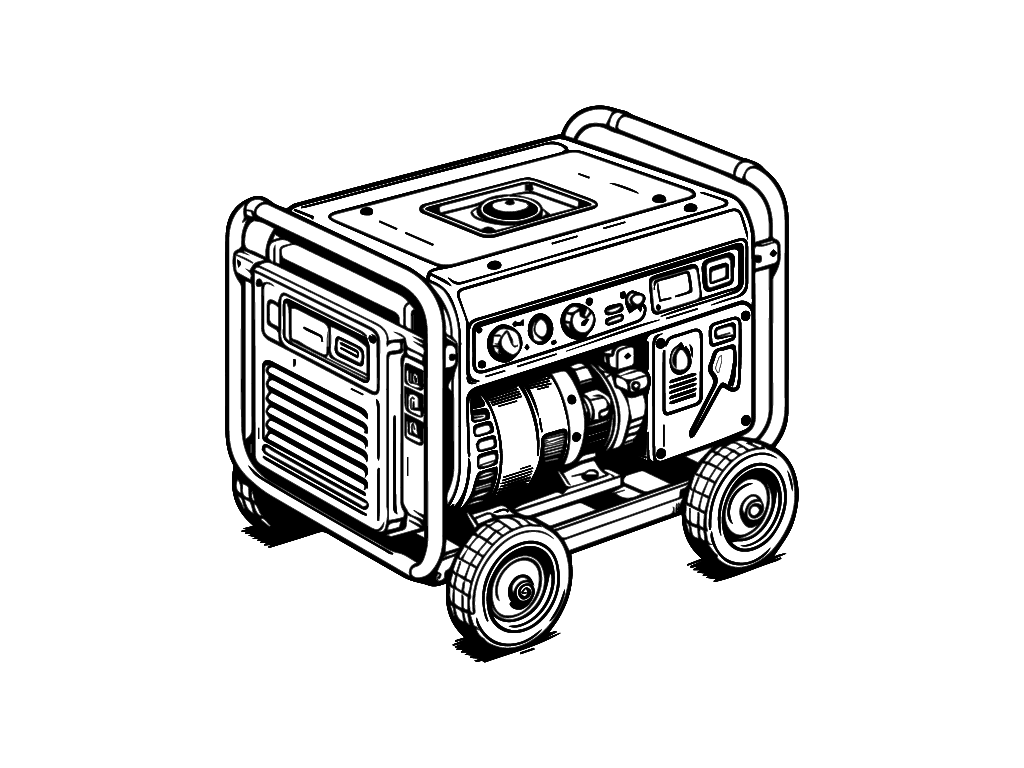
Fuel Generators: Traditional Might
When you need a big boost of electricity, it’s hard to beat fossil fuel generators. They can crank out a lot of energy in a very short time. All from a compact and affordable device.
You can choose between gasoline, diesel, or propane generators. Some can even accept more than one fuel type, including our favorite EcoFlow Smart Dual Fuel Generator. No matter which you choose, you don’t want to depend on it 100% to generate your energy, unless you have no other option.
Fuel generators are the easiest off-grid power solution. But they aren’t perfect. Pairing solar with fuel generators is usually the best off-grid power option.
Fuel Generator Basics
Fuel generators rely on a combustion engine. When the engine runs, it rotates a magnet within a set of coils in the alternator. This creates electricity we can use through electromagnetic induction.
The output is rated in watts. High-watt generators consume more fuel but also generate more electricity.
You can use generators to provide power to your devices or to charge a battery. The problem with powering devices directly is that the generator must always be running. And you’re certain to waste energy. Which means you’re wasting fuel. And money.
If you connect your fuel generator to a battery, it can absorb all of the energy produced. Plus, you can turn off the fuel generator and allow the battery to power your devices. Using a fuel generator with a solar generator works well. On days when solar doesn’t meet your needs, turn on the fuel generator to quickly charge the battery inside the solar generator.
Advantages of Fuel Generators
Here are the reasons why fuel generators are worth considering:
- Serious power: Fuel generators can produce a lot of electricity in a small amount of time.
- Affordable: The cost of the device is low but there are ongoing fuel and maintenance costs.
Because of the balance between low-cost and high-power, fuel generators can be useful for creating off-grid energy. They are excellent to have around as a backup source in case your primary source fails or can’t keep up with your needs.
Downsides to Fuel Generators
The issues with fuel generators include:
- Maintenance: The engine requires regular oil changes, filters, etc.
- Ongoing costs: Fuel generators have high recurring fuel costs.
- Pollution and noise: These two aspects will always be present when using a fuel generator.
The list of problems with fuel generators means they’re not great as your only energy source. But they’re still a worthy part of energy generation and excel as a backup solution.

Wind Turbine: Catching Air
You can make your electricity from a windmill. When using wind to generate electricity, it’s called a wind turbine. As the blades of the turbine spin, the generator/alternator converts the rotation to electricity.
Using wind to create off-grid energy can be a good solution if you:
- Live in an area with high average winds
- Have the space and ability to install it
Wind Energy Basics
Wind turbines work like fuel generators. Both rely on electromagnetic induction. Which is creating electrical current by spinning a magnet inside a set of coils. Turbines harness wind to spin the magnet.
The good news is that if you have enough wind, the spinning motion can be quite powerful.
The bad news is that if your property doesn’t get regular, powerful winds, it’s probably not going to work well. Locations in valleys or on the leeward side of a slope aren’t ideal.
Advantages of Wind Power
Created energy from wind can work well because:
- Sustainable energy: Wind is a plentiful natural resource to create renewable energy at home.
- Cost-effective: Operational costs are low. Initial cost is usually ~$1.50 per watt, less than solar.
- Complement solar: During winter months with less sunlight, the average wind speeds are higher.
Wind turbines can serve as a sustainable off-grid energy source in windy areas.
Downsides to Wind Power
The concerns related to wind energy include:
- Inconsistent: Power generation depends on wind, which can be inconsistent.
- Moving parts: Regular checks and maintenance are necessary to ensure function.
- Zoning issues: Tall wind turbines may not comply with local laws or regulations. Neighbors may also have concerns.
No energy source is perfect. For those with sustained winds and a good place to install them, wind might make sense. As solar prices have come down, many have opted to invest in solar instead. You can read more about wind power in this guide from the US Department of Energy.

Energy from Water: All About Flow
If you have a suitable water source, placing a turbine in flowing water can generate electricity. This is known as hydroelectric power.
Many people can’t consider this due to a lack of a suitable source. Local laws/regulations may also either prohibit it or make it too expensive to be worthwhile. If these problems don’t apply, it can be worth considering as an off-grid electrical solution.
Hydroelectric Basics
Once again, electromagnetic induction sits at the heart of most hydroelectric systems. Water flows through a turbine. The turbine connects to a generator/alternator and spins a magnet surrounded by coils. Flowing water changes into flowing electricity.
If you have a flowing water source, the work to install a hydroelectric turbine is relatively low. Other people can use a vertical drop to create flowing water. Gravity can pull water from an upper reservoir down to build flow and go through a turbine.
The more water and the stronger the flow, the more electricity you can create.
You can calculate the expected wattage of a hydroelectric source by:
- Find the vertical distance between the reservoir to the turbine (“head”), measured in feet.
- Know the volume of moving water (“flow”), measured in gallons per minute.
- Multiply the head by the flow, then divide by 10. The result is the watts.
For more, see this guide to planning a microhydropower system.
Advantages of Hydropower
Here are the main reasons people want to use water to create energy:
- Powerful: In the right conditions, hydropower offers a lot of electricity with minimal effort.
- Low operating costs: Once installed, the costs of this type of off-grid energy system can be very low.
When hydro works, it can work very well as a way to generate electricity to power your home.
Downsides to Hydropower
There are some major issues with hydropower, including:
- Regulatory hurdles: Between water rights, surveys, and other legal needs, hydroelectric is often not practical.
- Environmental impact: Disrupting water flow can cause a ripple effect.
Compared to other off-grid energy sources, using water is usually too difficult or impossible. It can be too expensive and time-consuming to get approval.

Biomass: Turning Waste to Electricity
If you have a lot of waste around, you may be able to use a biomass energy system to turn that waste into electrical power. At its heart, biomass is a steam engine that converts heat from burning fuel into usable electricity.
Most people can’t use these systems because they have high emissions and need significant fuel.
Biomass Energy Systems: Basics
Creating energy from garbage or waste starts with burnable natural materials like wood chips, crop byproducts, food scraps, and manure. Some places can use general garbage, but they use advanced emissions control systems. This is waste-to-energy incineration, popular in places like Denmark.
If you can find enough waste material, you burn it and use that to heat water. This turns into steam, which you send through a turbine. Which creates electricity through electromagnetic induction, just like wind and water power.
Advantages of Biomass Energy
The reasons biomass might be worth turning into electricity are:
- Waste reduction: Farms and others with a lot of organic waste can burn it for energy.
- Renewable fuel: You don’t have to drill or mine fossil fuels.
Downsides to Biomass Energy
The biggest downfalls to this electricity source are:
- Fuel supply: There’s no point in creating a waste-to-energy system unless you have a lot of fuel.
- Space requirements: Fuel must be stored and takes a lot of space.
- Emission concerns: Burning creates pollution that’s hard to minimize or control.
Because of these downsides, most people avoid waste-to-energy systems.

Other Off-Grid Energy Sources
The lion’s share of the best off-grid energy sources are solar, fuel generators, and wind turbines. Hydroelectric and waste-to-energy systems can be useful to a select few.
There are other ways to create electricity. They often don’t create a large enough energy supply to make it worthwhile. Let’s quickly go over these.
Human-Powered Kinetic Energy
If you spin anything, you can create some electricity. Hand cranks and pedal-based power systems are possible. But they’re very small scale.
A hand crank can provide enough power for a small radio or light. But you’d likely never depend on it as a major electricity source.
Pedal-powered machines can produce about 100 watts. That means one hour of biking would produce around 100 watt-hours of energy. Compared to one small 100W solar panel, it’s just not worthwhile. Except for serious emergency situations.
Thermoelectric or Geothermal Generators
Any heat source can create electricity. You can use heat sources to create steam and spin a turbine.
Or you can convert heat into electricity using the Seebeck effect. A controlled temperature difference can cause a voltage difference. Which means that electricity will flow.
The problem is that creating the heat source is usually not worth it just for producing electricity. And geothermal requires drilling and moving lots of water with pumps. Too intensive for personal needs. And still challenging at a larger scale.
Piezoelectric Devices
Another interesting emerging technology can create electricity from mechanical stress. Piezoelectric devices can turn your walking movement or vehicle traffic into electricity. They use specific materials that generate electricity when squeezed, twisted, or bent.
While it would be nice to rely on this as an off-grid energy source, it’s not a lot of power. And there are still plenty of issues with maintenance, cost, and general feasibility.
For now, this is more of an interesting talking point than a real off-grid energy source.

What Combination Is Best for You?
Creating your own electricity means taking a look at your needs and available options. By finding this balance, you’ll be able to create the off-grid energy supply you need.
Solar With Fuel Generator Backup
A solar panel array with a backup fuel generator is an excellent combination. It creates electricity that is reliable and consistent with low maintenance and operating costs. The biggest challenge is the startup cost of solar panels.
This can be ideal for an entirely off-grid situation. You primarily depend on solar power. If it doesn’t meet the demand, a small fuel generator can provide a boost.
It’s also perfect for a home backup system. If your outage lasts so long that the solar and batteries can’t keep up, turn on the fuel generator to charge the battery. Then turn it off to enjoy silent battery power.
Going with an EcoFlow Solar Generator (like the Delta Pro or Delta Pro Ultra) and the EcoFlow Smart Dual Fuel Generator is an amazing system. It’s instant, reliable, and very easy to work with. The generator cycles on and off automatically.
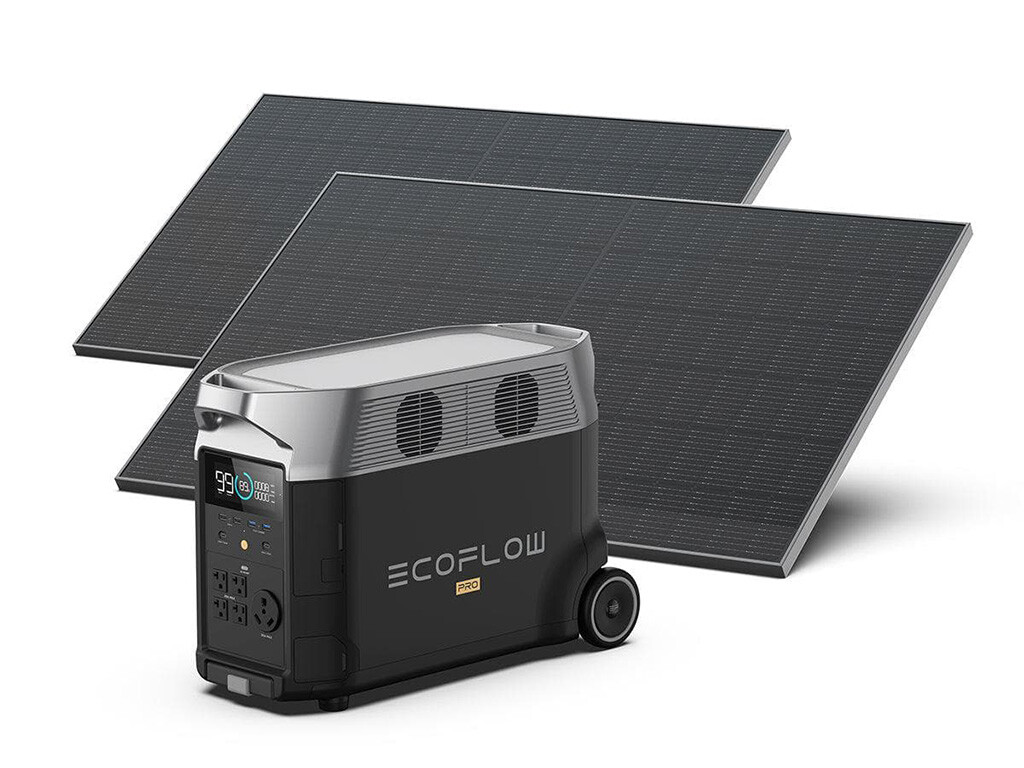

|
EcoFlow DELTA Pro Solar Generator with 2x 400W Panels |
Buy on EcoFlow |
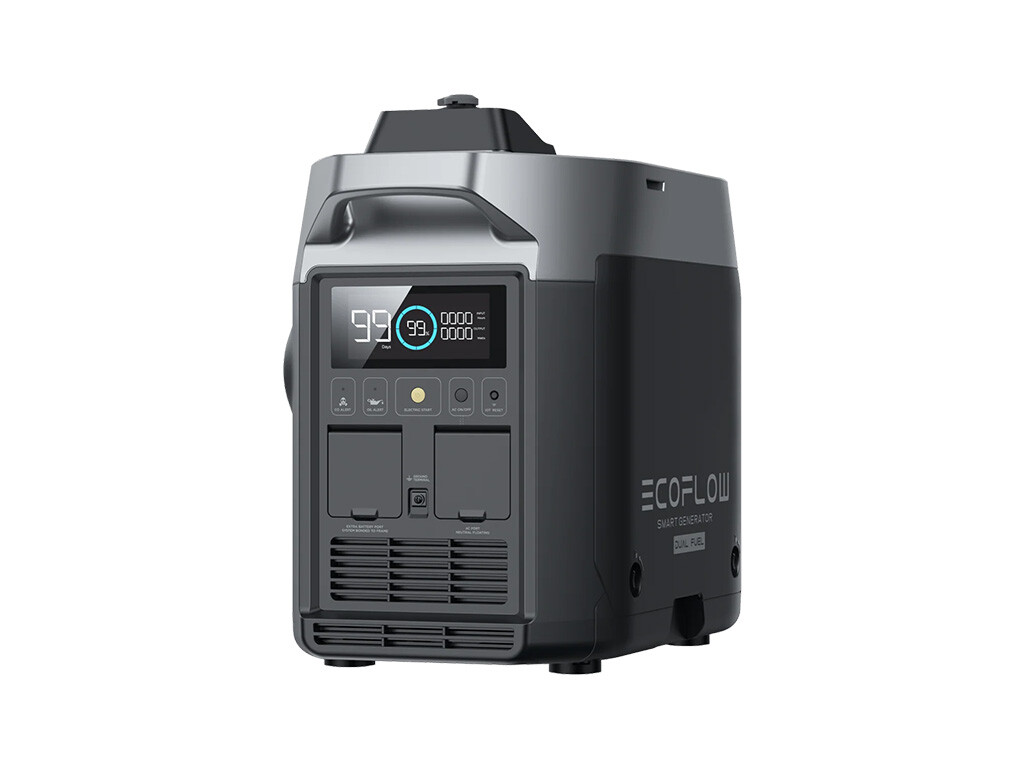

|
EcoFlow Dual Fuel Smart Generator |
DFSG on EcoFlow |
Solar and Wind
Solar power and wind turbines complement each other quite well. They have opposing cyclical patterns.
During the summer, sunlight is high while wind is low. Then during the winter, the situation reverses. The sun is lower but average wind speeds are up.
Many find that wind turbines aren’t worth the hassle. If you put that same investment into more solar, you’re likely going to have an easier time overall.
Hydro or Biomass with Solar or Fuel Generator
For those who are in the right position to implement hydroelectricity or a biomass system, it can still be a good idea to pair them with a backup. This takes some stress off leaving everything up to one system. In true off-grid fashion, redundancy is key.
You never know what might happen with a water source, even if you secure it with a reservoir. Dams break. Droughts come. And regulations change. The same is true for a biomass source. It may be abundant one year and nonexistent the next.
Using hydro or biomass with solar could be a good solution. And if you want to ramp up the stability, throw in a fuel generator for emergency backup too.

Putting It All Together
To make renewable energy at home, you most likely want to turn to a solar generator (battery system + solar panels) with a fuel generator backup. This can work as a complete off-grid system or to fill in when the grid fails.
Wind, hydro, and biomass may be attractive if your location allows.
If you’re ready for an instant solar generator system, head over to our post on the best whole-house solar generators. Get one kit and a fuel generator to create the power system of your dreams with two clicks.







