There are a lot of ways to create electrical systems. And two common approaches include portable power stations and inverters. While these two devices have a lot of things in common, they also are radically different.
In this article, we’ll help you understand the difference between a portable power station vs. an inverter. By showing what each one does along with the pros and cons of both, you’ll be able to make the right choice for your needs.
We carefully select the products and services we link to. If you buy through our links, we may earn a commission. There’s no extra cost to you and it helps us provide this information.

Portable Power Station Basics
Let’s kick things off by answering the question, “What is a portable power station?” You can tell a lot from the name. It is:
- Portable: Everything within one movable unit
- Power Station: Full-service system ready to capture and deliver electricity
Portable power stations are likely more complex than they appear at first glance. To pack all of the power station components into one portable unit, companies like EcoFlow and Bluetti combine a bit of engineering magic with design expertise.
The engineering aspects are what allows the power station to absorb, hold onto, and provide energy. This includes many different components, but the main ones are:
- Charge controllers to take in power from outlets, solar panels, and other energy sources
- Battery to hold power for you to use as needed
- AC inverter, outlets, and ports to provide power and connect your devices to
Before power stations were manufactured, the only option for off-grid power was to create a DIY electrical system. And many people still choose to go this route today.
But the designs of the portable power stations are nearly impossible to replicate. You could think of it like computers. Can you build a computer with your own parts? Absolutely! Will you be able to replicate a manufactured laptop with a DIY approach? Almost definitely not.
That’s basically what a power station is. They’re like the laptops of the off-grid energy world.
But today’s power stations are no longer just small compact units. While these 500W power stations still have a valid purpose, there are mega-sized home backup systems now too. And many options in between.
You could also say power stations are like a regular manufactured car, while using inverters to create a DIY system is like building a car from scratch. You’re going to need a lot of parts and knowledge to put it together yourself.
We are a premier outlet for power station information. Head over to our articles on specific power stations and brand overviews for more details, such as:
- Bluetti AC200MAX: Power, Performance, Modular
- EcoFlow River 2: Lightweight Champion of Portable Power
- Anker Comparison Chart: Full Anker Power Station Specs (And Power Banks)

|
EcoFlow DELTA Pro Ultra |
DPU on EcoFlow DPU on Amazon |

|
Jackery Explorer 1000 v2 Portable Power Station |
1000 v2 on Jackery 1000 v2 on Amazon |

|
BLUETTI AC200MAX Portable Power Station |
AC200MAX on Bluetti AC200MAX on Amazon |

Inverter Basics
An inverter, also known as a power inverter or AC inverter, is a specific device that plays a particular role within a solar, battery, or off-grid energy system.
The main purpose of an inverter is to change the direct current (DC) energy from sources like batteries and solar into alternating current (AC) energy that is fed through most outlets.
For most of your life, you’ve likely used AC energy without knowing it. That’s what comes out of most outlets in traditional grid-fed buildings and homes. In the US, this is typically 110V/120V, but it can also be 220V/240V (for large appliances).
But you’ve also used DC energy.
Your car’s battery is most likely a 12V DC battery. And you have tons of devices that plug into an AC outlet, but change it into a DC energy source. This applies to every USB-powered item, including your phone, tablet, e-reader, smartwatch, and more.
So where does the inverter come into play with this AC and DC discussion?
A power inverter is what is responsible for converting the DC power from solar panels or a battery into AC energy that can be fed into normal 110V/120V AC outlets. It converts (or inverts) the DC energy into AC energy.
The higher the inverter’s wattage, the more power it can provide through its AC outlets. As wattage goes up, so does price.
There are quite a few different types of inverters, so we’ll touch on those now. But one example of a popular inverter is the BougeRV 2,000W AC Pure Sine Wave Inverter.

|
BougeRV 2000W 12V Pure Sine Wave Inverter |
Buy on BougeRV |
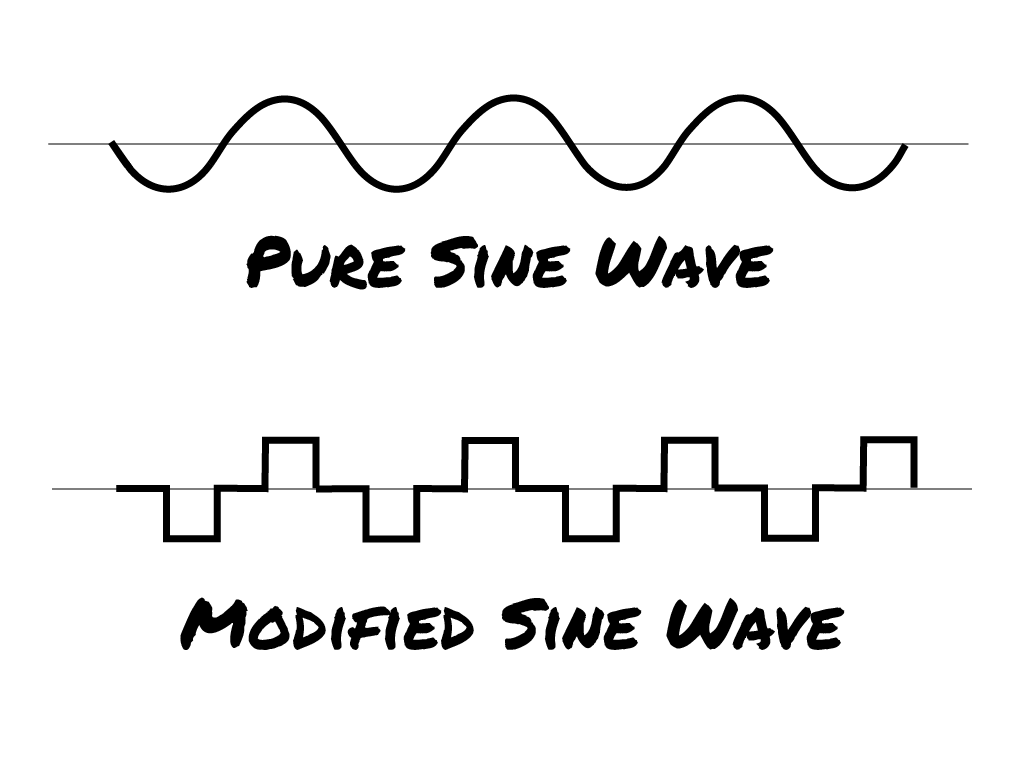
Pure Sine Wave vs. Modified Wave
Not all AC energy is the same. The “alternating” aspect of alternating current (AC) takes a lot of work to get right. When coming from a DC source like batteries, the inverter essentially flips the current back and forth very rapidly to achieve the AC result.
The cheaper and easier way to get from DC to AC is to use a modified wave inverter. Upon inspection, you’ll see rather large jumps between the current’s output wave. This can be acceptable for some devices, but it’s not great for sensitive electronics.
The better, cleaner, and more challenging (expensive) way is to use a pure sine wave (PSW) inverter.
A PSW inverter’s output looks more like a smooth curve. And it’s considered a cleaner energy source that sensitive electronics are designed to use.
Any high-quality power station, like the Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus, uses a PSW inverter. But you can find modified sine inverters on the market, including in some cheap power stations.

|
Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus Portable Power Station |
2000 Plus on Jackery 2000 Plus on Amazon |

Hybrid Inverters
Another type of inverter to be aware of is a hybrid inverter. These are pushing toward the power station capability by including multiple components into one device that goes far beyond the normal power inverter.
Hybrid inverters typically include the capability to:
- Accept power from DC sources like batteries and solar
- Feed power to AC circuits directly (rather than basic outlets)
The result is a very capable and useful type of inverter, especially for homes that use solar panels, battery backup, and grid electricity.
Hybrid inverters can usually maximize solar power generation by feeding it directly to AC circuits when needed, and if the AC demand is lower than the solar production, it feeds the excess into batteries. And in this way it acts like a solar charge controller.
Then whenever the AC circuits demand power (you turn on an appliance or plug something into a wall outlet), the hybrid inverter will feed from whatever source is available: solar, battery, or grid.
EG4 Hybrid Inverters are well-known as some of the best around.

|
EG4 Hybrid Inverter 18k PV 12kW AC |
Buy Now |

Inverter Generators
The last type of inverter is another product that combines an inverter with more components. This time with a traditional fuel generator that uses gasoline, diesel, or propane.
The inverter gets its power from the fuel-based engine, sort of like how most cars do, then feeds it through an AC inverter to run AC devices.
In a sense, the comparison between a portable power station vs. an inverter generator is about as close as you can get. They both are portable ways to produce energy away from the grid.
But a portable power station is much more versatile. It can use energy from almost any source, including fuel generators, as well as solar and standard AC outlets. They could do wind, car charging, and other off-grid energy sources as well. The DC input can be used for almost any DC source, as long as the specs are within the power station’s limits.
The biggest downside to inverter generators is that they only produce power when the engine is running. They also require a constant fuel source and regular maintenance. The upsides are that they’re generally cheaper and can provide a lot of power.
An inverter generator is a good solution if you need a lot of power for a short time. They do very poorly for things like charging cell phones or other low-power needs over long times.
There are many different inverter generators, but the Pulsar 2,200W Portable Dual Fuel Generator is one we recommend as an excellent balance between power and value.

|
Pulsar 2,200W Portable Dual Fuel Generator |
Buy on Amazon |

Do You Need a Power Station and an Inverter?
You don’t need a power station and an inverter because nearly every power station has an inverter built in.
It’s more of an either/or situation. Either you use a power station that has most everything you need in one box, OR you use an inverter and pair it with solar, batteries, and/or a fuel generator.
Sometimes you don’t need an inverter at all. Power stations include a variety of DC ports that don’t utilize the AC inverter. They can feed energy directly from solar panels to the battery to the DC ports. These DC ports include:
- USB-A ports, typically 15W to 18W
- USB-C ports, typically 30W to 100W
- 12V Car cigarette lighter outlets, usually 120W at most
- Anderson ports, often featuring high 30-amp output (~360W)
- DC 5521 and other types of barrel plugs
- Wireless charging pads
So if you have a power station and only want to run devices through these ports, you won’t use the inverter. And this comes with a major benefit: AC inverters use some power and essentially lower the time you can run your devices.
You can see more specifics about the ports and outlets of power stations on some of our posts covering them in detail, such as the Bluetti Comparison Chart: Specifications for Every Model article.

Similarities, Pros, and Cons
There’s a place for both portable power stations and power inverters. It just depends on what you are trying to do and what your priorities are.
Power stations and inverters are similar in many ways. They both:
- Can use DC energy sources like batteries
- Offer AC outlets for you to power AC devices
- Are rated in terms of maximum output Wattage
Yet there are also a lot of differences between power stations and inverters.
Power stations have a lot of benefits, but not everything is better. Here is a list of the pros and cons of portable power stations:
- Pros:
- Versatile product with most of the components you need for off-grid energy
- Designed by expert teams of engineers and are backed by long warranty coverage
- Are more portable than almost any DIY system using individual components
- Can be charged with AC power, solar, and other car chargers
- Cons:
- Power stations are usually more expensive than similar DIY systems
- You can’t customize each component and have to verify it has what you need
The pros and cons of inverters include:
- Pros:
- You can select the exact inverter that meets your needs and design around it
- Can often be used to power AC panel or circuits
- Cons:
- Does not include battery storage, charge controllers, and the necessary components to safely connect and use everything
- Requires extensive knowledge to create a usable system
In general, power stations are the more user-friendly and comprehensive energy system. They’re ready to go straight out of the box, simply plug in your power source to one side and your devices to the other. Inverters are one specific piece of equipment that can be used in a wider variety of applications, but requires other components and building the rest of the system.

The Amount of Power
Both portable power stations and power inverters can have varying amounts of power. They can range from small, lightweight options with around 500W or less of power, up to massive systems that can handle 5,000W (5kW) or more.
Every inverter, including those built into portable power stations, will have a rating that describes how much power it provides. This is given in watts, which is a rate of electrical flow (equal to one joule of energy per second).
One of the most important specifications is the main rating for an inverter. This is the continuous amount of power it can provide.
But most inverters also have surge or peak ratings as well, often double the continuous rating. This is usually for a very short period (fractions of a section) and helps with large startup power needs of some devices.
Small devices run on a low amount of watts. Large appliances and devices that use electricity to create heat need more watts. Here’s a list of devices and their approximate power consumption in watts:
- 10W to 50W: Phones, tablets, small fans, lights, and other lightweight devices
- 50W to 200W: Laptops, televisions, and small refrigerators
- 200W to 1,000W: Full size refrigerators, camping a/c units, desktop, computers, blenders, vacuum
- 1,000W to 3,000W: Air conditioner systems, induction cooktops, electric dryers
When buying an inverter, it’s important that you add up the watts of the devices you want to power. Then make sure to buy an inverter that can power those devices. The watts add up when you have things turned on at the same time. Be especially aware of the heavy-duty devices and their startup surge power needs.
Power Source
And don’t forget that there’s a crucial difference between the power available through an inverter and a power source.
An inverter is not a power source. It needs to pull energy in from a battery or another DC energy source. The inverter simply changes that power from DC into AC and feeds it out.
This is a crucial difference between the portable power station and an inverter. A power station can actually hold the stored energy in the battery. It can even charge the battery with solar panels. Then it uses the inverter to power the AC outlets.
An inverter must have an external power source.
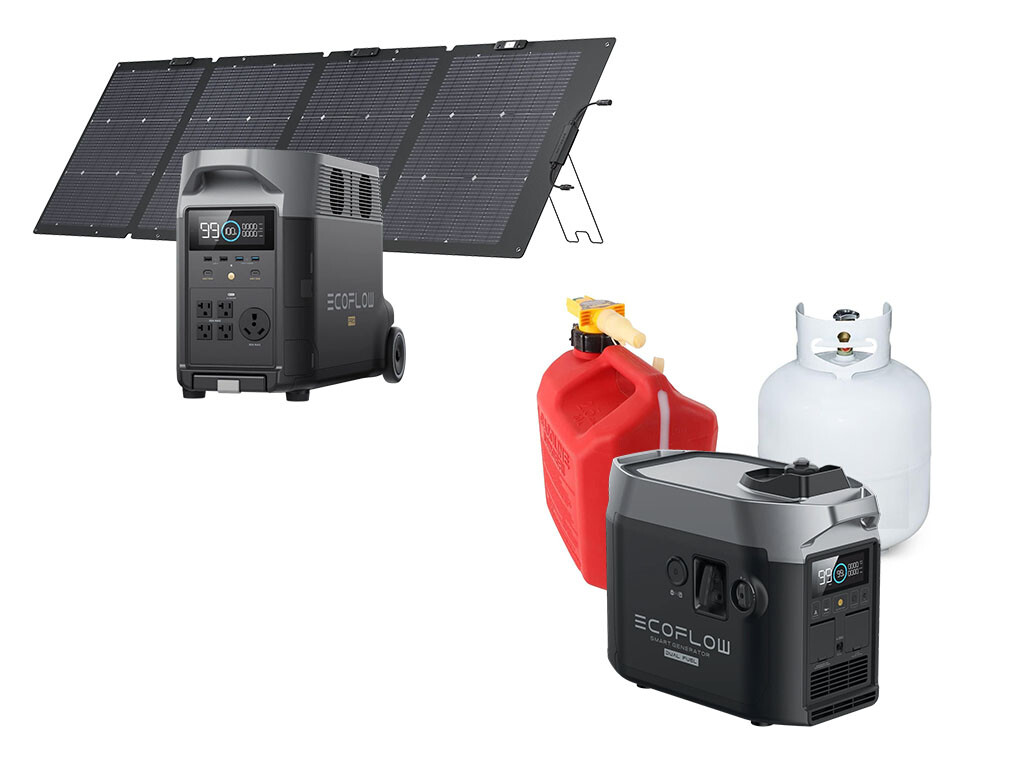

Solar Generator and Gas Generator
Another aspect of power stations that is confusing is their ability to work with other generators. When you connect a power station to a solar panel, you create what’s known as a solar generator. This term is somewhat interchangeable with portable power station (much to the chagrin of some generator traditionalists).
Now here’s the interesting part: You can pair a solar generator (or power station) with a traditional gas generator.
The reason you’d want to do this is because the gas generator can provide the energy, which the solar generator uses that energy to charge a battery and has a variety of outlets for you to plug your devices into, including ways to power an RV.
A pretty incredible setup is to use a solar generator (power station with solar panels) for most of your needs. You get the power from solar panels, then the power station charges the battery with that solar power, and you can use the inverter and other outlets on the power station as you need.
Solar is a great energy source that can even work at night (with battery storage). But it’s not perfect.
And if you need an extra boost when solar doesn’t cut it, a fuel generator can be a great choice. Fire up the engine and let that energy charge the power station’s battery. You will make very efficient use of the fuel generator’s output because your power station can absorb a lot of power quickly (depending on its specs). Then you can shut off the fuel generator and enjoy silent battery power.
Something like an EcoFlow Delta Pro 3 with a 4000W Dual Fuel Generator can be an ideal setup.
This idea is described in more detail in our post on a Dual Solar and Gas Generator.

|
EcoFlow DELTA Pro |
DP on EcoFlow DP on Amazon |

|
EcoFlow Dual Fuel Smart Generator |
DFSG on EcoFlow Buy on Amazon |

Wrap Up
An inverter changes DC power from a battery into AC power for normal outlets. It’s a piece of an energy system that must be used with other components to deliver AC power. A power station has an inverter, but also uses a built-in battery, charge controllers, and other items to create an energy source you can take anywhere.
Did you know that solar systems and battery storage can have serious tax benefits? Head over to our article on How the Portable Solar Generator Tax Credit Works to find out more details.
Want to see a head-to-head comparison of top power station brands? Our EcoFlow vs. Bluetti post is the quick rundown of two of the industry’s best brands.







