When you want or need to make sure an electronic device always has power, a UPS device is the tool for the job. The function of a UPS is to maintain a constant power supply without interruptions. In other words, UPS is used to create an uninterruptible power supply.
There are many different ways to achieve the function of a UPS, including a wide variety of dedicated UPS devices. Here at Solar Waypoint, our focus is on portable power stations and how they can keep your electronics powered up.
In this guide to the purpose of a UPS function, we’ll review what an uninterruptible power supply is, what you should look for with one, and how portable power stations are incorporating the need for an electronic UPS into their designs. We also have a full list of power stations with UPS functions.
We carefully select the products and services we link to. If you buy through our links, we may earn a commission. There’s no extra cost to you and it helps us provide this information.

UPS Basics
Let’s start off with a very short and simple overview of UPS basics.
What Does UPS Stand For?
The first thing to know is what UPS stands for. The abbreviation of UPS is for uninterruptible power supply. And we can break down this definition to see what that means:
- Uninterruptible: There should be no times when anything connected goes without power
- Power Supply: A device that provides an electrical output for another device
This simple UPS definition goes a long way at helping understand what a UPS does. But there’s a little more to the story.
The Function of a UPS
Now that you know what UPS means, let’s talk about what the actual purpose of a UPS is. Not everyone needs a UPS function, especially when it comes to portable power stations and solar generators.
A UPS is ideal for people that want to make sure that certain electronics will always remain powered on. Most of the time, people use a UPS to power things like:
- Desktop Computers
- WiFi Routers and Modems
- Medical Devices
- Server Racks
- Other Critical Infrastructure
By connecting these devices to the right uninterruptible power supply, they will always stay powered on.
Data and Device Protection
The need for some devices to always stay powered on is not just a mere convenience. Simply cutting off the power to certain sensitive electronics can cause data loss or damage to the unit. High-quality UPS devices avoid these problems even if a blackout rolls through.
It can also be an essential need. If you have a business that relies on specific electronics to function or remain secure, you need a UPS to avoid downtimes. And for certain medical devices like surgical instruments, it’s even more important.
A UPS is also necessary for more basic medical devices, like a CPAP that ensures you breathe safely overnight while sleeping. With the right UPS, your CPAP will keep rolling along and you won’t even notice an overnight outage.
No matter the device, the purpose of the UPS is to avoid the problems associated with power outages.
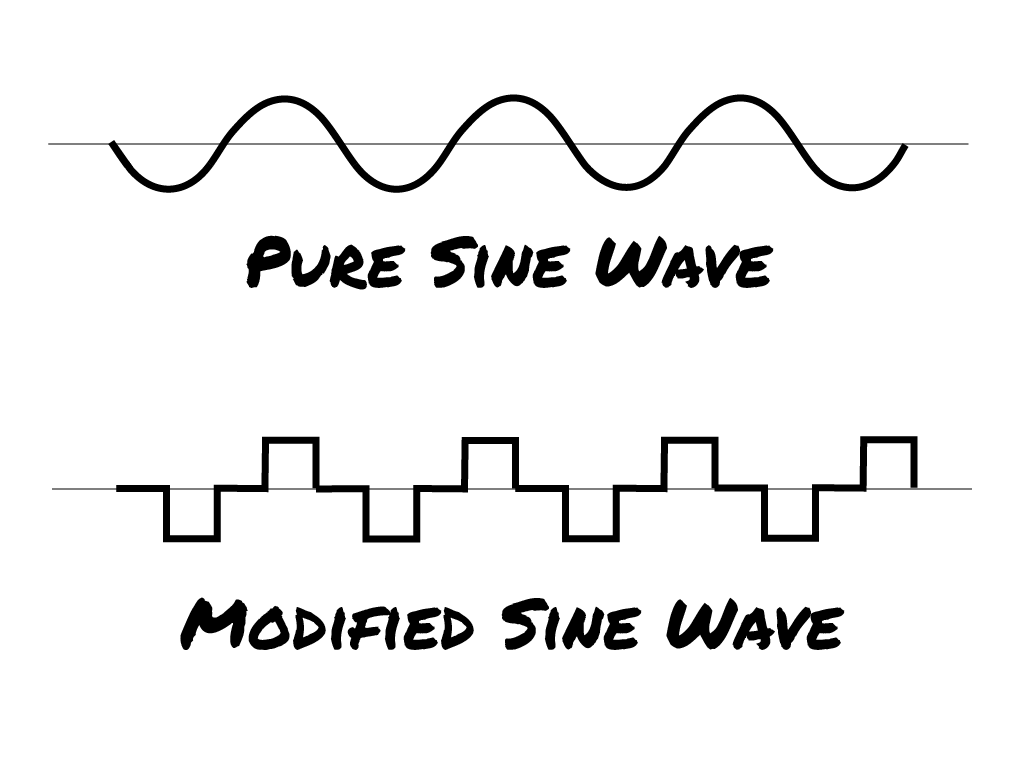
Clean Energy Supply
Another purpose of UPS devices is to ensure a clean energy supply. This means that it can deal with a variety of incoming energy fluctuations and output a constant energy supply that is more stable. You want to look for ones with a pure sine wave inverter.
Examples of potential fluctuations include:
- Voltage drops and overvoltage
- Power surges and brownouts
- Line noise and harmonic distortion
Not all UPS devices have this ability to provide a clean output energy. And not everyone needs this. If your utility company does a good job at providing clean power, then you shouldn’t have to worry about shelling out extra dough for features you don’t need. It’s more common to see this UPS function on high-end devices, especially those that are always online with a 0ms switchover time and designed to protect extremely expensive equipment.
In areas with poor energy supplies or major fluctuations, these UPS functions can be essential to protecting sensitive and expensive electronics. A UPS device can be a very important piece of home equipment in developing countries or ones with poorly maintained infrastructure.

How Does an Electrical Uninterruptible Power Supply Work?
A UPS device might sound too good to be true. How can anything always have power? Aren’t power outages and blackouts a concern? Where does the power come from?
These are all great questions to ask. And they’re also the exact problems that a UPS is designed to solve.
There are three primary features to any UPS device:
- Multiple Power Sources: A UPS combines external grid power with internal backup battery power
- Fast Switchover Time: The UPS must quickly switch from one power source to the other (or always be online)
- Charge Controller and Inverter: Internal components necessary to send power to and from an internal battery
By incorporating these two UPS features into one device, there can be a reliable source of power for the devices you want to constantly run.

Power Sources
The point of a UPS is not to provide an entirely off-grid power supply. It’s to make sure that a short-term backup energy source is there when external grid-supplied power fails.
The power sources for the most basic UPS devices is a basic combination of the wall outlet’s grid power and a small internal battery. You can use many different types of batteries (or even kinetic energy storage devices), but most UPS devices today use some type of lithium battery, such as NMC of LFP (LiFePO4).
A lot of generic UPS devices are designed for a very limited amount of backup power, somewhere around 10 to 30 minutes.
If you want to keep your devices powered up for a long time, you can either increase the size of your battery or add another off-grid energy source. In many industrial applications, this is usually done with a fuel generator, such as a large diesel or propane generator.
For smaller applications, portable power stations with larger batteries can be very useful. You can also add solar panels as an excellent power source, creating a solar generator. And if you set up your system correctly, you can use the solar power on a regular basis to lower your energy bill while also creating a backup power source that can generate electricity when the grid is down. The most important part of solar power is making sure you get the right amount of solar panels for your needs.
You can also use small fuel generators for home backup power too. Combining a solar generator and a fuel generator can be an excellent system.
UPS Switchover Time
A true UPS device will list a very important specification. This is the time it takes to switchover from grid power to the internal battery power (or generator power).
For sensitive electronics, this must be incredibly fast. If it’s not fast enough, your computer or server rack might not have enough power to stay on. It will rapidly shutdown and potentially lose data or worse. Even for things like a CPAP, a quick power outage can still reset the system and cause it to stop working.
The lowest UPS switchover time is 0ms. This is known as an “Online UPS” because it is always online. The way this is typically done is by always using the battery power. The grid input simply charges the battery and the battery sends power out. This seems simple enough. But it can be very taxing on the battery and other internal components.
In the world of residential UPS devices and portable power stations, it’s more common to find switchover times ranging from about 8ms to 30ms. This time is usually the maximum it will take to change from a failed grid power to the internal battery backup power. So if it’s rated at 10ms, it will do this switch in 10ms or less.
- 8ms to 10ms is considered incredibly fast. And for many computers, TVs, medical devices, and other electronics, 10ms is still fast enough that they stay powered on. But not always. The device manufacturer might have more information about how long it can stay powered on, but the best way (unfortunately) is to test it and find out. This is usually determined by the capacitors inside and how much energy they store.
- 20ms is still fast, but it is entering territory that might not be fast enough for extremely sensitive equipment. It might not a problem if you router shuts down real quick, yet it can pose a problem if you’re in the middle of a major project on your computer.
- 30ms is a little too slow for many devices to stay on. It’s a convenient way to make sure power is there and it automatically switches over, but many computers, TVs, and other devices will quickly shutdown if power cuts out for up to 30ms. This is more of a basic showing that you can use the device as a UPS without causing damage. Many power stations cannot be constantly plugged in on both sides without shortening the battery life.

Charge Controller and Inverter
It might sound like a UPS is very simple. Just an outlet and a battery, right?
In reality, there’s a pretty complicated structure inside that allows for the power to move between the multiple sources and the output. The two most important ones are:
- Charge Controllers: These allow the battery to absorb power from an AC source like a wall outlet or a DC source like solar panels or a fuel generator.
- AC Inverter: This is a critical piece of equipment that changes the battery’s DC energy into AC energy for the output.
Portable power stations always have these components, which makes them attractive devices to double as UPS devices. And while it used to be uncommon for power stations to have true UPS functions, that’s no longer the case. Now power stations from top brands like EcoFlow and Bluetti make sure to incorporate UPS function and fast switchover times in their top models. The EcoFlow Delta Pro Ultra even have an online 0ms UPS.
UPS vs. Backup Battery Power
You might think that a UPS sounds just like any backup battery power. And that perhaps any portable power station can serve as a UPS device. Unfortunately, that’s not the case.
Battery power can step in during outages to provide energy when the grid fails. That can be useful for things that you don’t mind if they shutoff momentarily. Maybe you want a backup power supply for your fridge. It’s acceptable if your fridge goes without power for a little time. You can even unplug it from the wall and plug it into your battery power supply. That’s not what a UPS is for.
The difference between a UPS device and general backup battery power is that a UPS will be used to constantly power the device. If a grid outage occurs, it will quickly switch over to the internal battery power. This fast and automatic switchover time is the key.
It’s also worth pointing out that some backup battery systems are NOT designed to continuously charge and discharge at the same time, if at all. Some will not allow output while charging. Others will cause damage to the battery if allowed to constantly do this. Some have pass-through power abilities but not true UPS functions.

Portable Power Stations With UPS Functions
We work hard to bring you the best information on portable power stations and solar generators. And in this section, we’ve compiled a list of portable power stations from brands we trust and recommend that incorporate UPS function.
The UPS switchover time is the most important element. It’s still very rare to find online 0ms UPS in a power station, but it does exist. EcoFlow used to be struggling with 30ms times, but the brand is now moving to an impressive 10ms time in its newest Delta 3 and River 3 power stations. Ones from Bluetti, Anker, and Jackery often have 20ms times. You’re more likely to find UPS functions on heavy-duty power stations made from home backup, but it can be found on smaller power stations too.
You may also want to check out our comparison charts to see more details from each brand, like this Anker Comparison Chart or Jackery Comparison Chart.
Here is a full chart of power stations where the manufacturer specifies the UPS function and maximum switchover time. We’ve included the battery size and inverter ratings because those are two critical part of a UPS device.
| Product | UPS / EPS | Battery | AC Output | Buy Now |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EcoFlow DELTA Pro Ultra | 0ms / 20ms | 6,000Wh | 7,200W | Buy Now |
| EcoFlow DELTA Pro 3 | 10ms | 4,096Wh | 4,000W | Buy Now |
| EcoFlow DELTA Pro | 30ms (EPS) | 3,600Wh | 3,600W | Buy Now |
| EcoFlow DELTA 2 Max | 30ms (EPS) | 2,048Wh | 2,400W | Buy Now |
| EcoFlow DELTA 3 Plus | 10ms | 1,024Wh | 1,800W | Buy Now |
| EcoFlow DELTA 3 | 10ms | 1,024Wh | 1,800W | Buy Now |
| EcoFlow DELTA 2 | 30ms (EPS) | 1,024Wh | 1,800W | Buy Now |
| EcoFlow RIVER 3 Plus | 10ms | 286Wh | 600W | Buy Now |
| EcoFlow RIVER 3 | 20ms | 245Wh | 300W | Buy Now |
| EcoFlow RIVER 2 Pro | 30ms (EPS) | 768Wh | 800W | Buy Now |
| EcoFlow RIVER 2 Max | 30ms (EPS) | 512Wh | 500W | Buy Now |
| EcoFlow RIVER 2 | 30ms (EPS) | 256Wh | 300W | Buy Now |
| BLUETTI EP900 | 10ms | 9,920Wh | 7,600W | Buy EP900 |
| BLUETTI EP800 | 10ms | 9,920Wh | 7,600W | Buy EP800 |
| BLUETTI EP500Pro | 0ms / 20ms | 5,120Wh | 3,000W | Buy EP500Pro |
| BLUETTI EP500 | 0ms / 20ms | 5,120Wh | 2,000W | Buy EP500 |
| Bluetti AC500 | 20ms | 3,072Wh | 5,000W | Buy AC500 |
| BLUETTI AC300 | 20ms | 3,072Wh | 3,000W | Buy AC300 |
| BLUETTI AC200L | 20ms | 2,048Wh | 2,400W | Buy AC200L |
| BLUETTI AC180T | 20ms | 1,433Wh | 1,800W | Buy AC180T |
| BLUETTI AC180P | 20ms | 1,440Wh | 1,800W | Buy 180P |
| BLUETTI AC180 | 20ms | 1152Wh | 1,800W | Buy AC180 |
| BLUETTI AC50B | 20ms | 448Wh | 700W | Buy AC50B |
| BLUETTI AC2A | 20ms | 205Wh | 300W | Buy AC2A |
| BLUETTI EB3A | 20ms | 269Wh | 600W | Buy EB3A |
| Jackery Explorer 3000 Pro | 20ms | 3,024Wh | 3,000W | Buy 3000 Pro |
| Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus | 20ms | 2,043Wh | 3,000W | Buy 2000 Plus |
| Jackery Explorer 1000 v2 | 20ms | 1,070Wh | 1,500W | Buy 1000 v2 |
| Jackery Explorer 600 Plus | 20ms | 632Wh | 800W | Buy 600 Plus |

Using a UPS
Most of the time when you want to give something constant power, you just plug it into the wall outlet and hope for the best. And when a grid blackout happens, you cross your fingers that it won’t last long.
With a UPS, you plug your critical device directly into the UPS device. Then the UPS plugs into the wall outlet.
An always-on (online) UPS will feed power from the grid to the battery, then from the battery to your devices.
Other offline UPS devices will serves as a pass-through power source most of the time. The grid power passes through the UPS and into the device you want to power, like your computer or medical device.
Then when the grid power fails, the UPS recognizes this and automatically switches over to its internal battery power. This is the heart of a UPS function and that’s why you need to have your devices plugged into the UPS to use them properly. It’s also why the UPS switchover time is a critical specification for any UPS.
Types of UPS Devices
There is an intricate world of different UPS types and technologies. We’ll quickly review some of these now, but since our focus is on the basic portable power station and how it works, this isn’t the focus of this article.
Here’s a quick list of different UPS terms and types:
- Double Conversion (Online): The UPS is always converting the energy twice, (1) wall outlet’s AC to the battery’s DC, then (2) from the battery’s DC to the power output’s AC. This results in a constant power supply always fed through the battery.
- Standby (Off-line): A more common UPS technology for small UPS devices, which uses the battery as a standby energy source to switch to when the grid power fails.
- Modular: A combination of smaller UPS devices used together, typically for larger scale power needs to create redundant systems.
- Motor Generator: The AC input actually powers a DC motor to charge the batteries, then the batteries keep the motor turning in an outage.
- Rotary: Same as Motor Generator, but without the battery. A fuel generator steps in during an outage instead.
- Single Phase: The type of power used by most end consumers and smaller power needs.
- Three Phase: The type of power generated by utility companies and used to transport electricity over long distances, used by large power consumers like data centers, hospitals, and other industrial applications.
- Split Phase: A type of UPS that can handle a mix of single and three phase power needs.
Some UPS devices use double-conversion.
Wrap Up: UPS Functions
The purpose of a UPS is to provide constant power through a grid outage. It stays plugged into a wall outlet to get power most of the time, then when a power outage or blackout happens, it uses battery power to run attached devices. Online UPS devices have no delay in power supply, but most consumer UPS devices are offline and have a switchover time from about 8ms to 30ms. It’s preferable to stay at 10ms or less for sensitive electronics.
Ready to discover more about the world of portable power stations? These devices go far beyond UPS functions and can serve as a power supply for your home, to add solar power to your RV, or go on a camping adventure with electricity.







